Methodological publications
- Methodological toolbox publications (also see citing Lead-DBS)
- Neudorfer, C., Butenko, K., Oxenford, S., Rajamani, N., Achtzehn, J., Goede, L., et al (2023). Lead-DBS v3.0: Mapping deep brain stimulation effects to local anatomy and global networks. NeuroImage.
- Horn, A., Li, N., Dembek, T. A., Kappel, A., Boulay, C., Ewert, S., et al. (2018). Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. NeuroImage.
- Horn A, Kühn AA (2015). Lead-DBS: A toolbox for deep brain stimulation electrode localizations and visualizations. NeuroImage.
- Horn, A., Kühn, A. A., Merkl, A., Shih, L., Alterman, R., & Fox, M. (2017). Probabilistic conversion of neurosurgical DBS electrode coordinates into MNI space. NeuroImage, 150, 395–404.
- Ewert, S., Plettig, P., Li, N., Chakravarty, M. M., Collins, D. L., Herrington, T. M., et al. (2017). Toward defining deep brain stimulation targets in MNI space: A subcortical atlas based on multimodal MRI, histology and structural connectivity. NeuroImage.
- Ewert, S., Horn, A., Finkel, F., Li, N., Kühn, A. A., & Herrington, T. M. (2018). Optimization and comparative evaluation of nonlinear deformation algorithms for atlas-based segmentation of DBS target nuclei. NeuroImage, 1–13.
- Husch, A., Petersen, M. V., Gemmar, P., Goncalves, J., & Hertel, F. (2017). PaCER – A fully automated method for electrode trajectory and contact reconstruction in deep brain stimulation. NeuroImage. Clinical, 17, 80–89.
- Dembek, T. A., Hoevels, M., Hellerbach, A., Horn, A., Petry-Schmelzer, J. N., Borggrefe, J., et al. (2019). Directional DBS leads show large deviations from their intended implantation orientation. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders.
- Treu, S., Strange, B., Oxenford, S., Kuehn, A., & Horn, A. (2020). Deep Brain Stimulation: Imaging on a group level, 142, 3086.
- Lofredi R, Auernig CG, Ewert S, Irmen F, Steiner LA, Scheller U, van Wijk BCM, Oxenford S, Kühn AA, Horn A. Interrater reliability of deep brain stimulation electrode localizations. NeuroImage. 2022.
- Lead Tutor paper for self-tutoring Lead-DBS
- SciRes-ID for the toolbox
- Lead Connectome methods publications
- Andreas Horn, Dirk Ostwald, Marco Reisert, and Felix Blankenburg (2013). The structural-functional connectome and the default mode network of the human brain. NeuroImage.
- Horn, A., & Blankenburg, F. (2016). Toward a standardized structural-functional group connectome in MNI space. NeuroImage, 124(Pt A), 310–322.
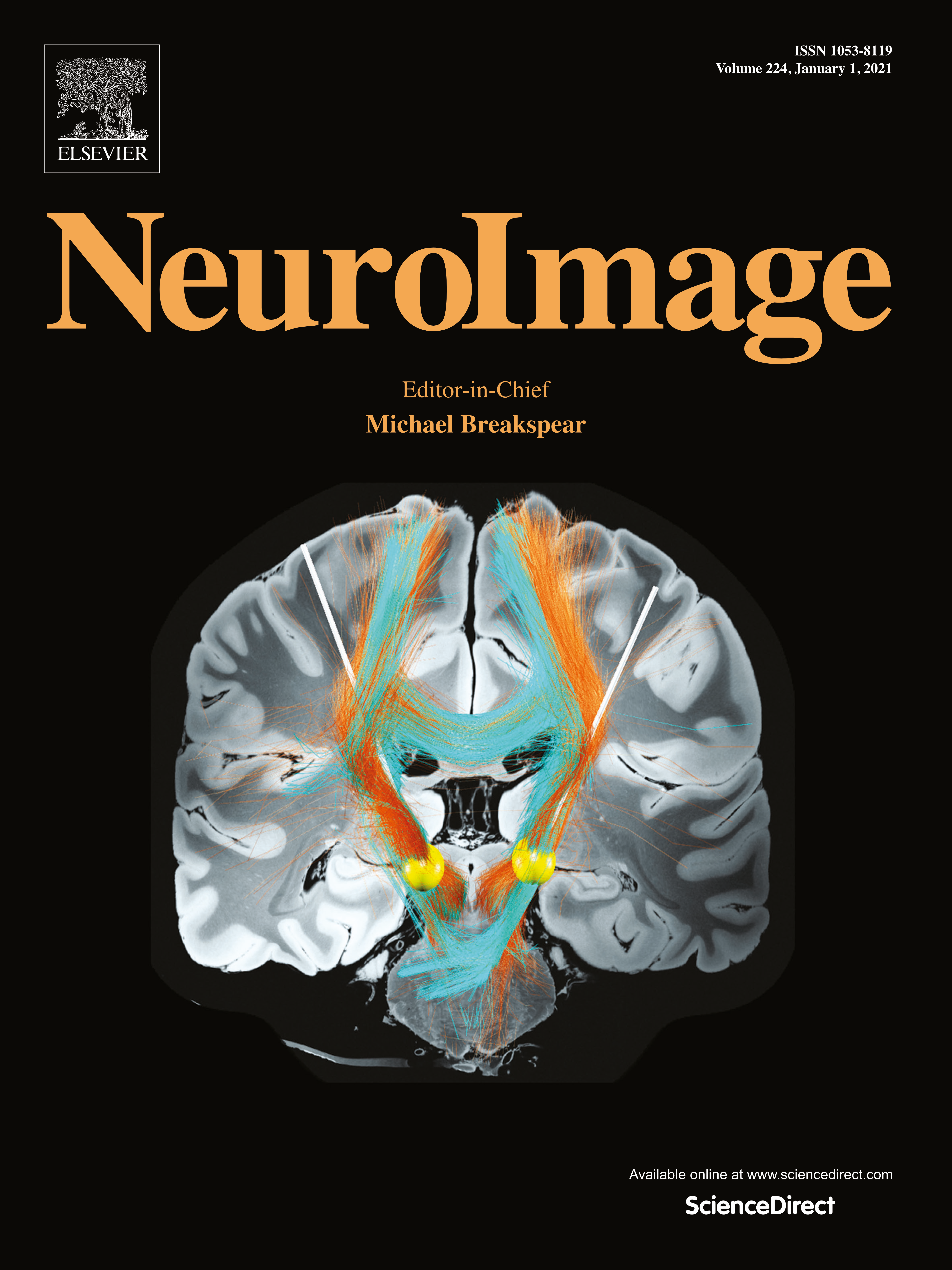
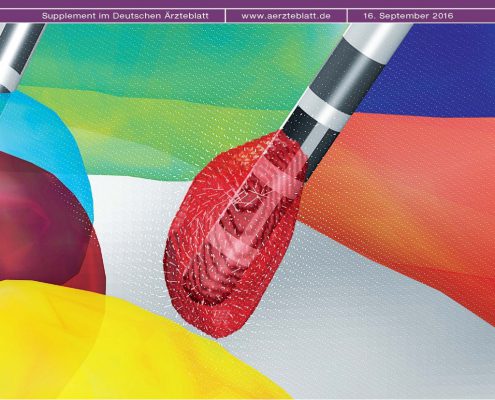
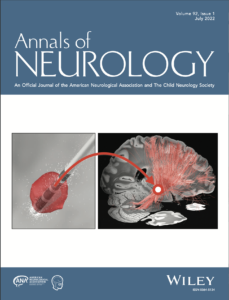
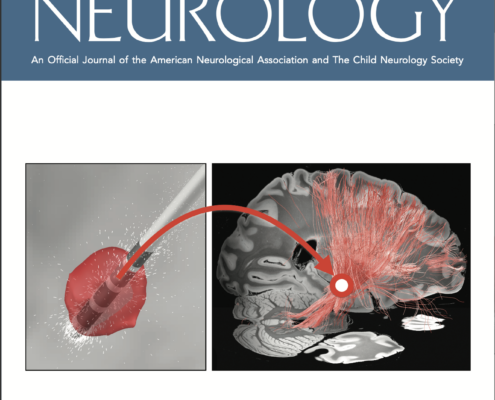
Cover Art
Applications of LEAD-DBS
Applications of Lead-Connectome
- Fox MD, Buckner RL, Liu H, Chakravarty MM, Lozano AM, Pascual-Leone A (2014) Resting-state networks link invasive and noninvasive brain stimulation across diverse psychiatric and neurological diseases. PNAS.
- Weigand A*, Horn A*, Caballero R, Cooke D, Stern AP, Taylor SF, Press D, Pascual-Leone A, Fox MD (2017) Prospective validation that subgenual connectivity predicts antidepressant efficacy of transcranial magnetic stimulation sites. Biological Psychiatry.
- Darby R, Horn A, Cushman F, Fox MD (2017) Lesion network localization of criminal behavior. PNAS.
-
Horn, A. (2015). A structural group-connectome in standard stereotactic (MNI) space. Data in Brief,
Did we miss a publication that used LEAD-DBS scientifically?